The Renaissance period which lasted from the century was a time of transformation in Europe’s cultural and intellectual scene. This era saw a resurgence of knowledge driven by the rediscovery of works, from ancient Greece and Rome. Additionally it brought about developments in art, philosophy and science. Renaissance art serves as a mirror of human cognitive advancement reflecting how people’s views of themselves and their place in the cosmos changed over time.
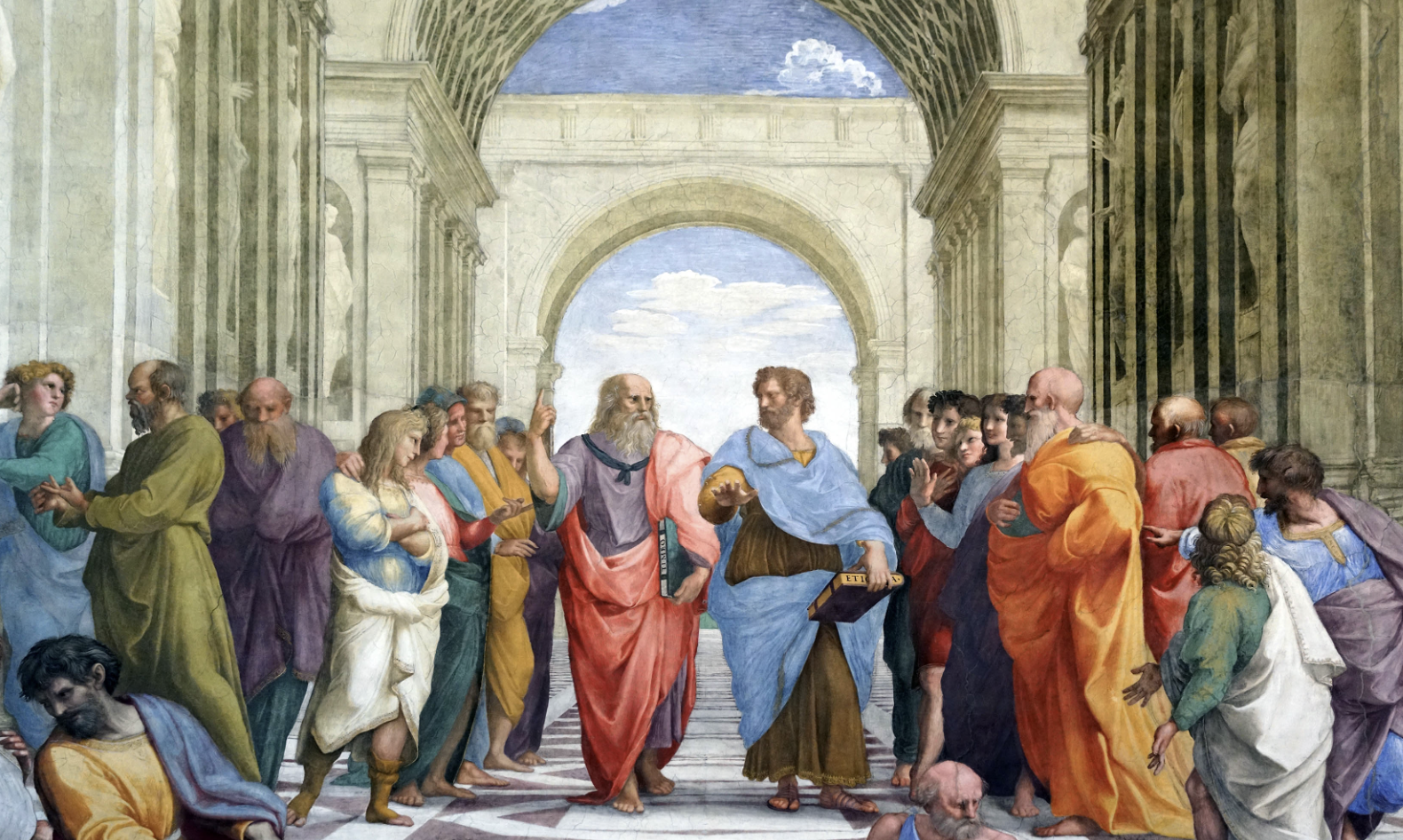

A key element of Renaissance art is its emphasis on realism and humanism closely linked to the shifts of that era. Prominent artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo and Raphael sought to depict reality with precision capturing details of human anatomy, movement and emotions. This quest for realism went beyond visual appeal; it stemmed from an interest in exploring the nuances of the human condition. Artists engaged in studying the body, dissecting cadavers and closely observing anatomical structures to accurately represent human forms in their works. This obsession with the body represented a move towards recognizing individuals and their experiences in understanding the world.
During the Renaissance there was a surge, in interest, in perception and sciences. Artists incorporated geometry and mathematics to add depth, perspective and dimensionality to their artworks. A significant breakthrough of this time was the introduction of perspective, which enabled artists to create the illusion of space on canvas. This approach marked progress, in terms of cognitive understanding by showcasing how the brain perceives relationships and depth. Filippo Brunelleschi, a skilled architect and engineer is credited with developing this technique; artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael utilized it to craft artworks that appeared lifelike and immersive.
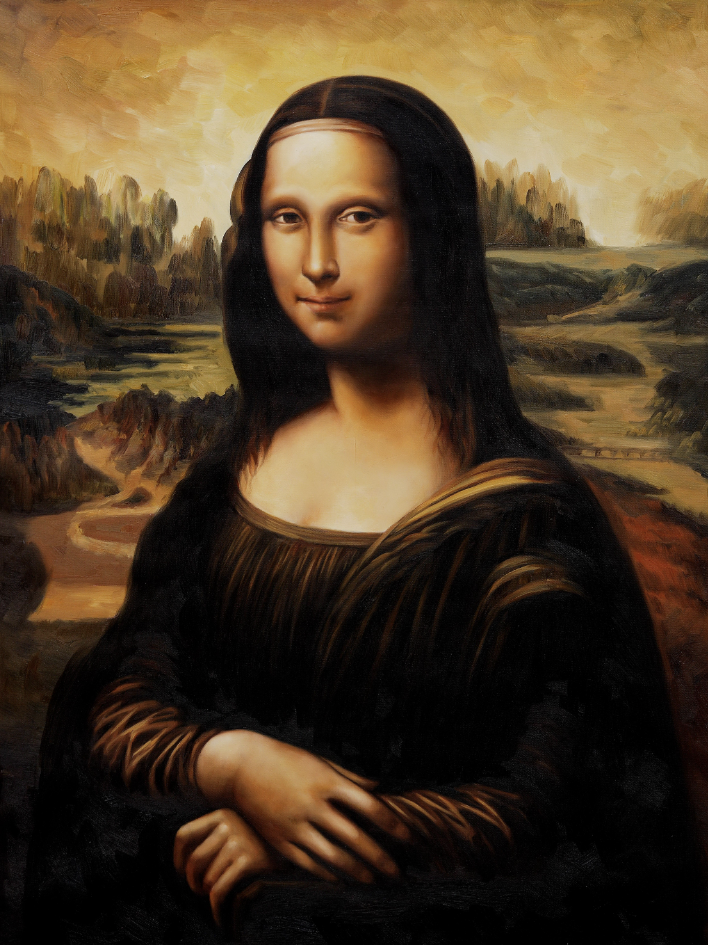
Furthermore Renaissance art reflected the period’s intrigue with emotions and psychology. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael sought not to achieve precision but also to capture the emotional essence of their subjects. Expressions, gestures and postures were crucial for conveying emotions, in art. Take da Vinci’s masterpiece, the Mona Lisa. With her enigmatic smile inviting viewers to explore the characters psyche more deeply. Similarly Michelangelo’s David not depicts the biblical hero’s physique but also expresses his emotional tension and anticipation at that moment. This emphasis on emotions represented a shift from viewing people as passive beings under divine control to recognizing them as active individuals with feelings and intellect.

Moreover during the Renaissance the emphasis on humanism which celebrated human worth and potential fostered a more reflective and introspective approach to life. The belief that individuals could shape their destinies and evolve through knowledge marked a departure from medieval views that prioritized divine intervention and concerns for the afterlife. Renaissance artists and scholars began exploring human nature and thought challenging norms and striving to understand minds, behaviors and the natural world through reasoning and observation.
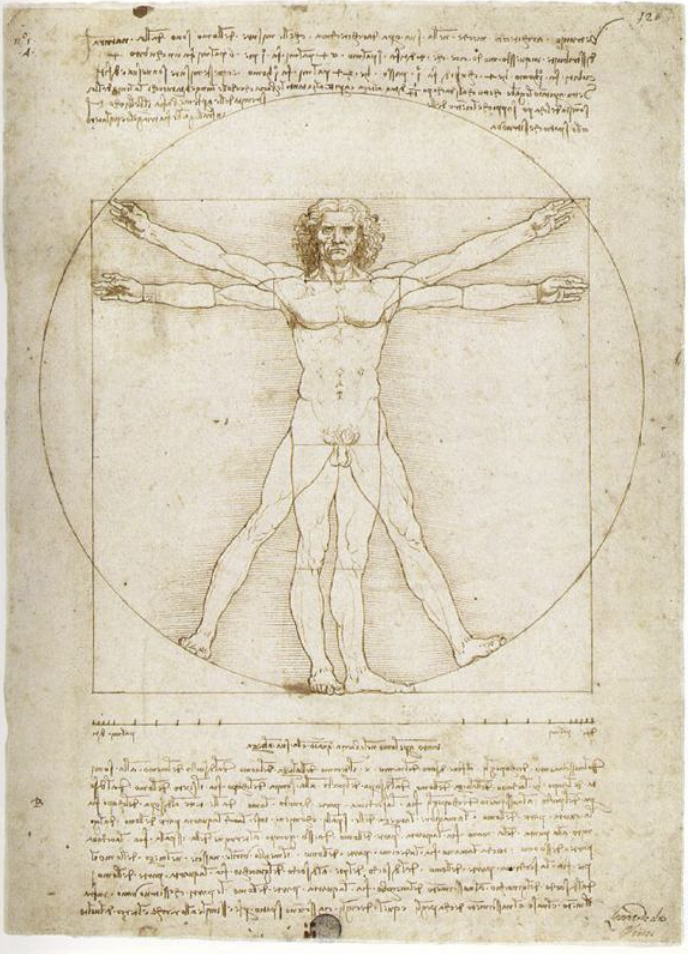
Additionally Renaissance art mirrored the changing perspectives, on the matters and the domain of science. With an influx of discoveries many artists found inspiration from nature and the world’s study. Leonardo da Vinci stands out for blending art with science; he was not a painter but also an inventor and scientist delving into anatomy, mechanics and natural sciences. For example his work Vitruvian Man illustrates the connection between the proportions of the body, and nature’s geometry, showcasing the convergence of art, mathematics and science.
Through their creations the exceptional artists of the Renaissance displayed an understanding of human cognition along with complexities related to perception, emotion and intellectual curiosity.
This era marked a chapter in the timeline of human thought where artistic expression and scientific breakthroughs converged to broaden knowledge horizons.
The impact of Renaissance art can be observed in sciences and psychology. The way artists from that period depicted human experiences with precision and emotional depth served as a foundation for research, in cognition and psychology. The link between art and sciences seen in the works of masters like Leonardo da Vinci continues, in times where art is both a reflection and a tool. For understanding human cognition.
In conclusion, Renaissance art transcends being a form; it also acts as a reflection of the evolution of human thought. The advancements made during that era in comprehending anatomy, emotions, perception and perspective highlight a deeper understanding of the human mind and its relationship with the world. Through their creations artists of the Renaissance showcased human creativity, intelligence and observational skills paving the way for revolutions in science and psychology that would follow later on.



